
About 600 CE the culture known as the “Redware people” arrived; little is known of them, however, beyond the red pottery they left. Alligator Pond in Manchester Parish and Little River in St. Ann Parish are among the earliest known sites of this Ostionoid person, who lived near the coast and extensively hunted turtles and fish.
Around 800 CE, Arawak arrived, eventually settling throughout the island. Living in villages ruled by tribal chiefs called the caciques, they sustained themselves on fishing and the cultivation of maize and cassava. At the height of their civilization, their population is estimated to have numbered as much as 60,000.
The Arawak brought from South America a system of raising yuca known as “conuco.” To add nutrients to the soil, the Arawak burned local bushes and trees and heaped the ash into large mounds, into which they then planted yuca cuttings. Most Arawak lived in large circular buildings (bohios), constructed with wooden poles, woven straw, and palm leaves. The Arawak spoke an Arawakan language and did not have writing. Some of the words used by them, such as barbacoa (“barbecue”), hamaca (“hammock”), kanoa (“canoe”), tabaco (“tobacco”), yuca, batata (“sweet potato”), and juracán (“hurricane”), have been incorporated into Spanish and English.
Spanish Jamaica

Christopher Columbus is believed to be the first European to reach Jamaica. He landed on the island on 5 May 1494, during his second voyage to the Americas. Columbus returned to Jamaica during his fourth voyage to the Americas. He had been sailing around the Caribbean nearly a year when a storm beached his ships in St. Ann’s Bay, Jamaica, on 25 June 1503. For a year Columbus and his men remained stranded on the island, finally departing in June 1504.
The Spanish crown granted the island to the Columbus family, but for decades it was something of a backwater, valued chiefly as a supply base for food and animal hides. In 1509 Juan de Esquivel founded the first permanent European settlement, the town of Sevilla la Nueva (New Seville), on the north coast. A decade later, Friar Bartolomé de las Casas wrote Spanish authorities about Esquivel’s conduct during the Higüey massacre of 1503.
In 1534 the capital was moved to Villa de la Vega (later Santiago de la Vega), now called Spanish Town. This settlement served as the capital of both Spanish and English Jamaica, from its founding in 1534 until 1872, after which the capital was moved to Kingston.
The Spanish enslaved many of the Arawak; some escaped, but most died from European diseases and overwork. The Spaniards also introduced the first African slaves. By the early 17th century, when virtually no Taino remained in the region, the population of the island was about 3,000, including a small number of African slaves. Disappointed in the lack of gold on the isle, the Spanish mainly used Jamaica as a military base to supply colonising efforts in the mainland Americas.
The Spanish colonists did not bring women in the first expeditions and took Taíno women for their common-law wives, resulting in mestizo children Sexual violence against the Taíno women by the Spanish was also common.
British Invasion
In late 1654, English leader Oliver Cromwell launched the Western Design armada against Spain’s colonies in the Caribbean. In April 1655, General Robert Venables led the armada in an attack on Spain’s fort at Santo Domingo, Hispaniola. After the Spanish repulsed this poorly-executed attack, the English force then sailed for Jamaica, the only Spanish West Indies island that did not have new defensive works. In May 1655, around 7,000 English soldiers landed near Jamaica’s Spanish Town capital and soon overwhelmed the small number of Spanish troops (at the time, Jamaica’s entire population only numbered around 2,500). Spain never recaptured Jamaica, losing the Battle of Ocho Rios in 1657 and the Battle of Rio Nuevo in 1658. In 1660, the turning point was when some Spanish runaway slaves, who became Jamaican Maroons, switched sides from the Spanish to the English For England, Jamaica was to be the ‘dagger pointed at the heart of the Spanish Empire,’ although in fact it was a possession of little economic value then. England gained formal possession of Jamaica from Spain in 1670 through the Treaty of Madrid. Removing the pressing need for constant defense against Spanish attack, this change served as an incentive to planting.
British Colonisation
Cromwell increased the island’s European population by sending indentured servants and prisoners to Jamaica. Due to the wars in Ireland at this time two-thirds of this 17th-century European population was Irish. But tropical diseases kept the number of Europeans under 10,000 until about 1740. Although the African slave population in the 1670s and 1680s never exceeded 10,000, by the end of the 17th century imports of slaves increased the black population to at least five times the number of whites. Thereafter, Jamaica’s African population did not increase significantly in number until well into the 18th century, in part because ships coming from the west coast of Africa preferred to unload at the islands of the Eastern Caribbean. At the beginning of the 18th century, the number of slaves in Jamaica did not exceed 45,000, but by 1800 it had increased to over 300,000.
House of Assembly of Jamaica
Beginning with the Stuart monarchy’s appointment of a civil governor to Jamaica in 1661, political patterns were established that lasted well into the 20th century. The second governor, Lord Windsor, brought with him in 1662 a proclamation from the king giving Jamaica’s non-slave populace the rights of English citizens, including the right to make their own laws. Although he spent only ten weeks in Jamaica, Lord Windsor laid the foundations of a governing system that was to last for two centuries: a crown-appointed governor acting with the advice of a nominated council in the legislature. The legislature consisted of the governor and an elected but highly unrepresentative House of Assembly. For years, the planter-dominated Assembly was in continual conflict with the various governors and the Stuart kings; there were also contentious factions within the assembly itself. For much of the 1670s and 1680s, Charles II and James II and the assembly feuded over such matters as the purchase of slaves from ships not run by the royal English trading company. The last Stuart governor, Christopher Monck, 2nd Duke of Albemarle, who was more interested in treasure hunting than in planting, turned the planter oligarchy out of office. After the duke’s death in 1688, the planters, who had fled Jamaica to London, succeeded in lobbying James II to order a return to the pre-Albemarle political arrangement (the local control of Jamaican planters belonging to the assembly).
Jamaica’s pirates
Following the 1655 conquest, Spain repeatedly attempted to recapture Jamaica. In response, in 1657, Governor Edward D’Oyley invited the Brethren of the Coast to come to Port Royal and make it their home port. The Brethren was made up of a group of pirates who were descendants of cattle-hunting boucaniers (later Anglicised to buccaneers), who had turned to piracy after being robbed by the Spanish (and subsequently thrown out of Hispaniola). These pirates concentrated their attacks on Spanish shipping, whose interests were considered the major threat to the town. These pirates later became legal English privateers who were given letters of marque by Jamaica’s governor. Around the same time that pirates were invited to Port Royal, England launched a series of attacks against Spanish shipping vessels and coastal towns. By sending the newly appointed privateers after Spanish ships and settlements, England had successfully set up a system of defense for Port Royal. Jamaica became a haven of privateers, buccaneers, and occasionally outright pirates: Christopher Myngs, Edward Mansvelt, and most famously, Henry Morgan.
England gained formal possession of Jamaica from Spain in 1670 through the Treaty of Madrid. Removing the pressing need for constant defense against Spanish attack, this change served as an incentive to planting. This settlement also improved the supply of slaves and resulted in more protection, including military support, for the planters against foreign competition. As a result, the sugar monoculture and slave-worked plantation society spread across Jamaica throughout the 18th century, decreasing Jamaica’s dependence on privateers for protection and funds.
However, the English colonial authorities continued to have difficulties suppressing the Spanish Maroons, who made their homes in the mountainous interior, and mounted periodic raids on estates and towns, such as Spanish Town. The Karmahaly Maroons continued to stay in the forested mountains, and periodically fought the English.
Another blow to Jamaica’s partnership with privateers was the violent earthquake which destroyed much of Port Royal on 7 June 1692. Two-thirds of the town sank into the sea immediately after the main shock. After the earthquake, the town was partially rebuilt but the colonial government was relocated to Spanish Town, which had been the capital under Spanish rule. Port Royal was further devastated by a fire in 1703 and a hurricane in 1722. Most of the sea trade moved to Kingston. By the late 18th century, Port Royal was largely abandoned.
18th century and Jamaica’s sugar boom
In the mid-17th century, sugarcane had been brought into the British West Indies by the Dutch, from Brazil. Upon landing in Jamaica and other islands, they quickly urged local growers to change their main crops from cotton and tobacco to sugarcane. With depressed prices of cotton and tobacco, due mainly to stiff competition from the North American colonies, the farmers switched, leading to a boom in the Caribbean economies. Sugarcane was quickly snapped up by the British, who used it in cakes and to sweeten tea. In the 18th century, sugar replaced piracy as Jamaica’s main source of income. The sugar industry was labour-intensive and the British brought hundreds of thousands of enslaved Africans to Jamaica. By 1832, the median-size plantation in Jamaica had about 150 slaves, and nearly one of every four bondsmen lived on units that had at least 250 slaves. In The Book of Night Women, author Marlon James indicates that the ratio of slave owner to enslaved Africans is 1:33 James also depicts atrocities that slave owners subjected slaves to, and violent resistance from the slaves; numerous slaves died in pursuit of freedom. After slavery was abolished in 1834, sugarcane plantations used a variety of forms of labour including workers imported from India under contracts of indenture.
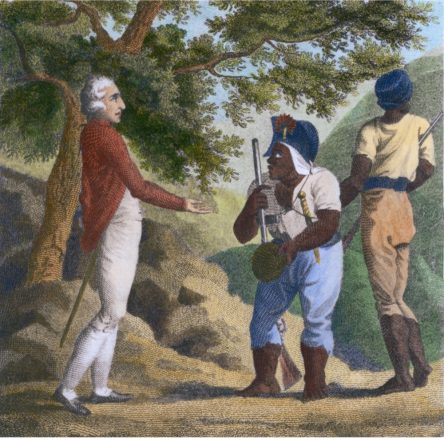
First Maroon War
When the British captured Jamaica in 1655, the Spanish colonists fled, leaving a large number of African slaves. These former Spanish slaves created three Palenques, or settlements. Former slaves organised under the leadership of Juan de Serras allied with the Spanish guerrillas on the western end of the Cockpit Country, while those under Juan de Bolas established themselves in modern-day Clarendon Parish and served as a “black militia” for the English. The third chose to join those who had previously escaped from the Spanish to live and intermarry with the Arawak people. Each group of Maroons established distinct independent communities in the mountainous interior of Jamaica. They survived by subsistence farming and periodic raids of plantations. Over time, the Maroons came to control large areas of the Jamaican interior Early in the 18th century, the Maroons took a heavy toll on the British troops and local militia sent against them in the interior, in what came to be known as the First Maroon War.
The First Maroon War came to an end with a 1739–40 agreement between the Maroons and the British government. The Maroons were to remain in their five main towns (Accompong; Cudjoe’s Town (Trelawny Town); Nanny Town, later known as Moore Town; Scott’s Hall (Jamaica); and Charles Town, Jamaica), living under their own rulers and a British supervisor. In exchange, they were asked to agree not to harbour new runaway slaves, but rather to help catch them. This last clause in the treaty naturally caused a split between the Maroons and the rest of the black population, although from time to time runaways from the plantations still found their way into Maroon settlements. Another provision of the agreement was that the Maroons would serve to protect the island from invaders. The latter was because the Maroons were revered by the British as skilled warriors. The person responsible for the compromise with the British was the Leeward Maroon leader, Cudjoe, a short, almost dwarf-like man who for years fought skillfully and bravely to maintain his people’s independence. As he grew older, however, Cudjoe became increasingly disillusioned. He ran into quarrels with his lieutenants and with other Maroon groups. He felt that the only hope for the future was honorable peace with the enemy, which was just what the British were thinking. The 1739 treaty should be seen in this light. A year later, the even more rebellious Windward Maroons of Trelawny Town also agreed to sign a treaty under pressure from both white Jamaicans and the Leeward Maroons.
Tacky’s revolt

By Everett Collection
In May 1760, Tacky, a slave overseer on the Frontier plantation in Saint Mary Parish, led a group of enslaved Africans in taking over the Frontier and Trinity plantations while killing their enslavers. They then marched to the storeroom at Fort Haldane, where the munitions to defend the town of Port Maria were kept. After killing the storekeeper, Tacky and his men stole nearly 4 barrels of gunpowder and 40 firearms with shot, before marching on to overrun the plantations at Heywood Hall and Esher. By dawn, hundreds of other slaves had joined Tacky and his followers. At Ballard’s Valley, the rebels stopped to rejoice in their success. One slave from Esher decided to slip away and sound the alarm Obeahmen (Caribbean witch doctors) quickly circulated around the camp dispensing a powder that they claimed would protect the men from injury in battle and loudly proclaimed that an Obeahman could not be killed. Confidence was high. Soon there were 70 to 80 mounted militia on their way along with some Maroons from Scott’s Hall, who were bound by treaty to suppress such rebellions. When the militia learned of the Obeahman’s boast of not being able to be killed, an Obeahman was captured, killed and hung with his mask, ornaments of teeth and bone and feather trimmings at a prominent place visible from the encampment of rebels. Many of the rebels, confidence shaken, returned to their plantations. Tacky and 25 or so men decided to fight on. Tacky and his men went running through the woods being chased by the Maroons and their legendary marksman, Davy the Maroon. While running at full speed, Davy shot Tacky and cut off his head as evidence of his feat, for which he would be richly rewarded. Tacky’s head was later displayed on a pole in Spanish Town until a follower took it down in the middle of the night. The rest of Tacky’s men were found in a cave near Tacky Falls, having committed suicide rather than going back to slavery.
Second Maroon War
In 1795, the Second Maroon War was instigated when two Maroons were flogged by a black slave for allegedly stealing two pigs. When six Maroon leaders came to the British to present their grievances, the British took them as prisoners. This sparked an eight-month conflict, spurred by the fact that Maroons felt that they were being mistreated under the terms of Cudjoe’s Treaty of 1739, which ended the First Maroon War. The war lasted for five months as a bloody stalemate. The British 5,000 troops and militia outnumbered the Maroons ten to one, but the mountainous and forested topography of Jamaica proved ideal for guerrilla warfare. The Maroons surrendered in December 1795. A treaty signed in December between Major General George Walpole and the Maroon leaders established that the Maroons would beg on their knees for the King’s forgiveness, return all runaway slaves, and be relocated elsewhere in Jamaica. The governor of Jamaica ratified the treaty, but gave the Maroons only three days to present themselves to beg forgiveness on 1 January 1796. Suspicious of British intentions, most of the Maroons did not surrender until mid-March. The British used the contrived breach of treaty as a pretext to deport the entire Trelawny Town Maroons to Nova Scotia. After a few years the Maroons were again deported to the new British settlement of Sierra Leone in West Africa.
Baptist War
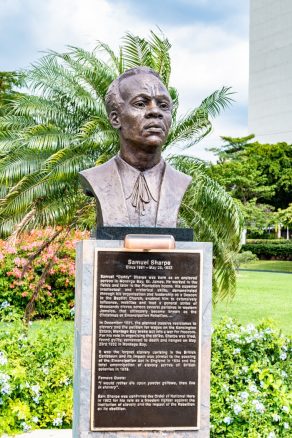
In 1831, enslaved Baptist preacher Samuel Sharpe led a strike among demanding more freedom and a working wage of “half the going wage rate.” Upon refusal of their demands, the strike escalated into a full rebellion, in part because Sharpe had also made military preparations with a rebel military group known as the Black Regiment led by a slave known as Colonel Johnson of Retrieve Estate, about 150 strong with 50 guns among them. Colonel Johnson’s Black Regiment clashed with a local militia led by Colonel Grignon at old Montpelier on December 28. The militia retreated to Montego Bay while the Black Regiment advanced an invasion of estates in the hills, inviting more slaves to join while burning houses, fields and other properties, setting off a trail of fires through the Great River Valley in Westmoreland and St. Elizabeth to St James.
The Baptist War, as it was known, became the largest slave uprising in the British West Indies, lasting 10 days and mobilised as many as 60,000 of Jamaica’s 300,000 slaves. The rebellion was suppressed by British forces under the control of Sir Willoughby Cotton. The reaction of the Jamaican Government and plantocracy was far more brutal. Approximately five hundred slaves were killed in total: 207 during the revolt and somewhere in the range between 310 and 340 slaves were killed through “various forms of judicial executions” after the rebellion was concluded, at times, for quite minor offences (one recorded execution indicates the crime being the theft of a pig; another, a cow). An 1853 account by Henry Bleby described how three or four simultaneous executions were commonly observed; bodies would be allowed to pile up until workhouse slaves carted the bodies away at night and buried them in mass graves outside town. The brutality of the plantocracy during the revolt is thought to have accelerated the process of emancipation, with initial measures beginning in 1833.
Emancipation
Because of the loss of property and life in the 1831 Baptist War rebellion, the British Parliament held two inquiries. Their reports on conditions contributed greatly to the abolition movement and passage of the 1833 law to abolish slavery as of August 1, 1834, throughout the British Empire. The Jamaican slaves were bound (indentured) to their former owners’ service, albeit with a guarantee of rights, until 1838 under what was called the “Apprenticeship System”.
With the abolition of the slave trade in 1808 and slavery itself in 1834, however, the island’s sugar- and slave-based economy faltered. The period after emancipation in 1834 initially was marked by a conflict between the plantocracy and elements in the Colonial Office over the extent to which individual freedom should be coupled with political participation for blacks. In 1840 the assembly changed the voting qualifications in a way that enabled a majority of blacks and people of mixed race (browns or mulattos) to vote. But neither change in the political system, nor abolition of slavery changed the planter’s chief interest, which lay in the continued profitability of their estates, and they continued to dominate the elitist assembly. Nevertheless, at the end of the 19th century and in the early years of the 20th century, the crown began to allow some Jamaicans – mostly local merchants, urban professionals, and artisans—into the appointed councils.
The Morant Bay Rebellion
Tensions resulted in the October 1865 Morant Bay rebellion led by Paul Bogle. The rebellion was sparked on 7 October, when a black man was put on trial and imprisoned for allegedly trespassing on a long-abandoned plantation. During the proceedings, James Geoghegon, a black spectator, disrupted the trial, and in the police’s attempts to seize him and remove him from the courthouse, a fight broke out between the police and other spectators. While pursuing Geoghegon, the two policeman were beaten with sticks and stones. The following Monday arrest warrants were issued for several men for rioting, resisting arrest, and assaulting the police. Among them was Baptist preacher Paul Bogle. A few days later on 11 October, Mr. Paul Bogle marched with a group of protesters to Morant Bay. When the group arrived at the court house they were met by a small and inexperienced volunteer militia. The crowd began pelting the militia with rocks and sticks, and the militia opened fire on the group, killing seven black protesters before retreating.
Governor John Eyre sent government troops, under Brigadier-General Alexander Nelson, to hunt down the poorly armed rebels and bring Paul Bogle back to Morant Bay for trial. The troops met with no organised resistance, but regardless they killed blacks indiscriminately, most of whom had not been involved in the riot or rebellion: according to one soldier, “we slaughtered all before us… man or woman or child”. In the end, 439 black Jamaicans were killed directly by soldiers, and 354 more (including Paul Bogle) were arrested and later executed, some without proper trials. Paul Bogle was executed “either the same evening he was tried or the next morning.” Other punishments included flogging for over 600 men and women (including some pregnant women), and long prison sentences, with thousands of homes belonging to black Jamaicans were burned down without any justifiable reason.
George William Gordon, a Jamaican businessman and politician, who had been critical of Governor John Eyre and his policies, was later arrested by Governor John Eyre who believed he had been behind the rebellion. Despite having very little to do with it, Gordon was eventually executed. Though he was arrested in Kingston, he was transferred by Eyre to Morant Bay, where he could be tried under martial law. The execution and trial of Gordon via martial law raised some constitutional issues back in Britain, where concerns emerged about whether British dependencies should be ruled under the government of law, or through military license. The speedy trial saw Gordon hanged on 23 October, just two days after his trial had begun. He and William Bogle, Paul’s brother, “were both tried together, and executed at the same time.
Decline of the sugar industry
During most of the 18th century, a monocrop economy based on sugarcane production for export flourished. In the last quarter of the century, however, the Jamaican sugar economy declined as famines, hurricanes, colonial wars, and wars of independence disrupted trade. By the 1820s, Jamaican sugar had become less competitive with that from high-volume producers such as Cuba and production subsequently declined. By 1882 sugar output was less than half the level achieved in 1828. A major reason for the decline was the British Parliament’s 1807 abolition of the slave trade, under which the transportation of slaves to Jamaica after 1 March 1808 was forbidden; the abolition of the slave trade was followed by the abolition of slavery in 1834 and full emancipation within four years. Unable to convert the ex-slaves into a sharecropping tenant class similar to the one established in the post-Civil War South of the United States, planters became increasingly dependent on wage labour and began recruiting workers abroad, primarily from India, China, and Sierra Leone. Many of the former slaves settled in peasant or small farm communities in the interior of the island, the “yam belt,” where they engaged in subsistence and some cash crop farming.
 The second half of the 19th century was a period of severe economic decline for Jamaica. Low crop prices, droughts, and disease led to serious social unrest, culminating in the Morant Bay rebellions of 1865. However, renewed British administration after the 1865 rebellion, in the form of crown colony status, resulted in some social and economic progress as well as investment in the physical infrastructure. Agricultural development was the centrepiece of restored British rule in Jamaica. In 1868 the first large-scale irrigation project was launched. In 1895 the Jamaica Agricultural Society was founded to promote more scientific and profitable methods of farming. Also in the 1890s, the Crown Lands Settlement Scheme was introduced, a land reform program of sorts, which allowed small farmers to purchase two hectares or more of land on favourable terms.
The second half of the 19th century was a period of severe economic decline for Jamaica. Low crop prices, droughts, and disease led to serious social unrest, culminating in the Morant Bay rebellions of 1865. However, renewed British administration after the 1865 rebellion, in the form of crown colony status, resulted in some social and economic progress as well as investment in the physical infrastructure. Agricultural development was the centrepiece of restored British rule in Jamaica. In 1868 the first large-scale irrigation project was launched. In 1895 the Jamaica Agricultural Society was founded to promote more scientific and profitable methods of farming. Also in the 1890s, the Crown Lands Settlement Scheme was introduced, a land reform program of sorts, which allowed small farmers to purchase two hectares or more of land on favourable terms.
Between 1865 and 1930, the character of landholding in Jamaica changed substantially, as sugar declined in importance. As many former plantations went bankrupt, some land was sold to Jamaican peasants under the Crown Lands Settlement whereas other cane fields were consolidated by dominant British producers, most notably by the British firm Tate and Lyle. Although the concentration of land and wealth in Jamaica was not as drastic as in the Spanish-speaking Caribbean, by the 1920s the typical sugar plantation on the island had increased to an average of 266 hectares. But, as noted, smallscale agriculture in Jamaica survived the consolidation of land by sugar powers. The number of small holdings in fact tripled between 1865 and 1930, thus retaining a large portion of the population as peasantry. Most of the expansion in small holdings took place before 1910, with farms averaging between two and twenty hectares.
The rise of the banana trade during the second half of the 19th century also changed production and trade patterns on the island. Bananas were first exported in 1867, and banana farming grew rapidly thereafter. By 1890, bananas had replaced sugar as Jamaica’s principal export. Production rose from 5 million stems (32 percent of exports) in 1897 to an average of 20 million stems a year in the 1920s and 1930s, or over half of domestic exports. As with sugar, the presence of American companies, like the well-known United Fruit Company in Jamaica, was a driving force behind renewed agricultural exports. The British also became more interested in Jamaican bananas than in the country’s sugar. Expansion of banana production, however, was hampered by serious labour shortages. The rise of the banana economy took place amidst a general exodus of up to 11,000 Jamaicans a year.
Jamaica as a Crown Colony
In 1846 Jamaican planters, adversely affected by the loss of slave labour, suffered a crushing blow when Britain passed the Sugar Duties Act, eliminating Jamaica’s traditionally favoured status as its primary supplier of sugar. The Jamaica House of Assembly stumbled from one crisis to another until the collapse of the sugar trade, when racial and religious tensions came to a head during the Morant Bay rebellion of 1865. Although suppressed ruthlessly, the severe rioting so alarmed the planters that the two-centuries-old assembly voted to abolish itself and asked for the establishment of direct British rule. In 1866 the new governor John Peter Grant arrived to implement a series of reforms which accompanied the transition to a crown colony. The government consisted of the Legislative Council and the executive Privy Council containing members of both chambers of the House of Assembly, but the Colonial Office exercised effective power through a presiding British governor. The council included a few handpicked prominent Jamaicans for the sake of appearance only. In the late 19th century, crown colony rule was modified; representation and limited self-rule were reintroduced gradually into Jamaica after 1884. The colony’s legal structure was reformed along the lines of English common law and county courts, and a constabulary force was established. The smooth working of the crown colony system was dependent on a good understanding and an identity of interests between the governing officials, who were British, and most of the nonofficial, nominated members of the Legislative Council, who were Jamaicans. The elected members of this body were in a permanent minority and without any influence or administrative power. The unstated alliance – based on shared color, attitudes, and interest – between the British officials and the Jamaican upper class was reinforced in London, where the West India Committee lobbied for Jamaican interests. Jamaica’s white or near-white propertied class continued to hold the dominant position in every respect; the vast majority of the black population remained poor and unenfranchised.
Marcus Garvey

Marcus Mosiah Garvey, a black activist and Trade Unionist, founded the Universal Negro Improvement Association and African Communities League in 1914, one of Jamaica’s first political parties in 1929, and a workers association in the early 1930s. Garvey also promoted the Back-to-Africa movement, which called for those of African descent to return to the homelands of their ancestors. Garvey, to no avail, pleaded with the colonial government to improve living conditions for indigenous peoples in the West Indies. Garvey, a controversial figure, had been the target of a four-year investigation by the United States government. He was convicted of mail fraud in 1923 and had served most of a five-year term in an Atlanta penitentiary when he was deported to Jamaica in 1927. Garvey left the colony in 1935 to live in the United Kingdom, where he died heavily in debt five years later. He was proclaimed Jamaica’s first national hero in the 1960s after Edward P.G. Seaga, then a government minister, arranged the return of his remains to Jamaica. In 1987 Jamaica petitioned the United States Congress to pardon Garvey on the basis that the federal charges brought against him were unsubstantiated and unjust.
Rastafari movement

The Rastafari movement, a new religion, emerged among impoverished and socially disenfranchised Afro-Jamaican communities in 1930s Jamaica. Its Afrocentric ideology was largely a reaction against Jamaica’s then-dominant British colonial culture. It was influenced by both Ethiopianism and the Back-to-Africa movement promoted by black nationalist figures like Marcus Garvey. The movement developed after several Christian clergymen, most notably Leonard Howell, proclaimed that the crowning of Haile Selassie as Emperor of Ethiopia in 1930 fulfilled a Biblical prophecy. By the 1950s, Rastafari’s counter-cultural stance had brought the movement into conflict with wider Jamaican society, including violent clashes with law enforcement. In the 1960s and 1970s it gained increased respectability within Jamaica and greater visibility abroad through the popularity of Rasta-inspired reggae musicians like Bob Marley. Enthusiasm for Rastafari declined in the 1980s, following the deaths of Haile Selassie and Marley.
The Great Depression and worker protests
The Great Depression caused sugar prices to slump in 1929 and led to the return of many Jamaicans. Economic stagnation, discontent with unemployment, low wages, high prices, and poor living conditions caused social unrest in the 1930s. Uprisings in Jamaica began on the Frome Sugar Estate in the western parish of Westmoreland and quickly spread east to Kingston. Jamaica, in particular, set the pace for the region in its demands for economic development from British colonial rule.
Because of disturbances in Jamaica and the rest of the region, the British in 1938 appointed the Moyne Commission. An immediate result of the Commission was the Colonial Development Welfare Act, which provided for the expenditure of approximately Ł1 million a year for twenty years on coordinated development in the British West Indies. Concrete actions, however, were not implemented to deal with Jamaica’s massive structural problems.
New unions and parties
The rise of nationalism, as distinct from island identification or desire for self-determination, is generally dated to the 1938 labour riots that affected both Jamaica and the islands of the Eastern Caribbean. William Alexander Bustamante, a moneylender in the capital city of Kingston who had formed the Jamaica Trade Workers and Tradesmen Union (JTWTU) three years earlier, captured the imagination of the black masses with his messianic personality, even though he himself was light-skinned, affluent, and aristocratic. Bustamante emerged from the 1938 strikes and other disturbances as a populist leader and the principal spokesperson for the militant urban working class, and in that year, using the JTWTU as a stepping stone, he founded the Bustamante Industrial Trade Union (BITU), which inaugurated Jamaica’s workers movement.
A distant cousin of Bustamante’s, Norman W. Manley, concluded as a result of the 1938 riots that the real basis for national unity in Jamaica lay in the masses. Unlike the union-oriented Bustamante, however, Manley was more interested in access to control over state power and political rights for the masses. On 18 September 1938, he inaugurated the People’s National Party (PNP), which had begun as a nationalist movement supported by the mixed-race middle class and the liberal sector of the business community with leaders who were highly educated members of the upper middle class. The 1938 riots spurred the PNP to unionise labour, although it would be several years before the PNP formed major labour unions. The party concentrated its earliest efforts on establishing a network both in urban areas and in banana-growing rural parishes, later working on building support among small farmers and in areas of bauxite mining.
The PNP adopted a socialist ideology in 1940 and later joined the Socialist International, allying itself formally with the social democratic parties of Western Europe. Guided by socialist principles, Manley was not a doctrinaire socialist. PNP socialism during the 1940s was similar to British Labour Party ideas on state control of the factors of production, equality of opportunity, and a welfare state, although a left-wing element in the PNP held more orthodox Marxist views and worked for the internationalisation of the trade union movement through the Caribbean Labour Congress. In those formative years of Jamaican political and union activity, relations between Manley and Bustamante were cordial. Manley defended Bustamante in court against charges brought by the British for his labour activism in the 1938 riots and looked after the BITU during Bustamante’s imprisonment.
Bustamante had political ambitions of his own, however. In 1942, while still incarcerated, he founded a political party to rival the PNP, called the Jamaica Labour Party (JLP). The new party, whose leaders were of a lower class than those of the PNP, was supported by conservative businessmen and 60,000 dues-paying BITU members, who encompassed dock and sugar plantation workers and other unskilled urban labourers. On his release in 1943, Bustamante began building up the JLP. Meanwhile, several PNP leaders organised the leftist-oriented Trade Union Congress (TUC). Thus, from an early stage in modern Jamaica, unionised labour was an integral part of organised political life.
For the next quarter century, Bustamante and Manley competed for centre stage in Jamaican political affairs, the former espousing the cause of the “barefoot man”; the latter, “democratic socialism,” a loosely defined political and economic theory aimed at achieving a classless system of government. Jamaica’s two founding fathers projected quite different popular images. Bustamante, lacking even a high school diploma, was an autocratic, charismatic, and highly adept politician; Manley was an athletic, Oxford-trained lawyer, Rhodes scholar, humanist, and liberal intellectual. Although considerably more reserved than Bustamante, Manley was well liked and widely respected. He was also a visionary nationalist who became the driving force behind the crown colony’s quest for independence.
Following the 1938 disturbances in the West Indies, London sent the Moyne Commission to study conditions in the British Caribbean territories. Its findings led in the early 1940s to better wages and a new constitution. Issued on 20 November 1944, the Constitution modified the crown colony system and inaugurated limited self-government based on the Westminster model of government and universal adult suffrage. It also embodied the island’s principles of ministerial responsibility and the rule of law. Thirty-one percent of the population participated in the 1944 elections. The JPL – helped by its promises to create jobs, its practice of dispensing public funds in pro-JLP parishes, and the PNP’s relatively radical platform – won an 18 percent majority of the votes over the PNP, as well as 22 seats in the 32-member House of Representatives, with 5 going to the PNP and 5 to other short-lived parties. In 1945 Bustamante took office as Jamaica’s first premier (the pre-independence title for head of government).
Under the new charter, the British governor, assisted by the six-member Privy Council and ten-member Executive Council, remained responsible solely to the crown. The Jamaican Legislative Council became the upper house, or Senate, of the bicameral Parliament. House members were elected by adult suffrage from single-member electoral districts called constituencies. Despite these changes, ultimate power remained concentrated in the hands of the governor and other high officials
The road to independence
After World War II, Jamaica began a relatively long transition to full political independence. Jamaicans preferred British culture over American, but they had a love-hate relationship with the British and resented British domination, racism, and the dictatorial Colonial Office. Britain gradually granted the colony more self-government under periodic constitutional changes. Jamaica’s political patterns and governmental structure were shaped during two decades of what was called “constitutional decolonisation,” the period between 1944 and independence in 1962.
Having seen how little popular appeal the PNP’s 1944 campaign position had, the party shifted toward the centre in 1949 and remained there until 1974. The PNP actually won a 0.8-percent majority of the votes over the JLP in the 1949 election, although the JLP won a majority of the House seats. In the 1950s, the PNP and JLP became increasingly similar in their sociological composition and ideological outlook. During the cold war years, socialism became an explosive domestic issue. The JLP exploited it among property owners and churchgoers, attracting more middle-class support. As a result, PNP leaders diluted their socialist rhetoric, and in 1952 the PNP moderated its image by expelling four prominent leftists who had controlled the TUC. The PNP then formed the more conservative National Workers Union (NWU). Henceforth, PNP socialism meant little more than national planning within a framework of private property and foreign capital. The PNP retained, however, a basic commitment to socialist precepts, such as public control of resources and a more equitable income distribution. Manley’s PNP came to office for the first time after winning the 1955 elections with an 11-percent majority over the JLP and 50.5 percent of the popular vote.
Amendments to the constitution that took effect in May 1953 reconstituted the Executive Council and provided for eight ministers to be selected from among House members. The first ministries were subsequently established. These amendments also enlarged the limited powers of the House of Representatives and made elected members of the governor’s executive council responsible to the legislature. Manley, elected chief minister beginning in January 1955, accelerated the process of decolonisation during his able stewardship. Further progress toward self-government was achieved under constitutional amendments in 1955 and 1956, and cabinet government was established on 11 November 1957.
Assured by British declarations that independence would be granted to a collective West Indian state rather than to individual colonies, Manley supported Jamaica’s joining nine other British territories in the West Indies Federation, established on 3 January 1958. Manley became the island’s premier after the PNP again won a decisive victory in the general election in July 1959, securing thirty of forty-five House seats.
Membership in the federation remained an issue in Jamaican politics. Bustamante, reversing his previously supportive position on the issue, warned of the financial implications of membership – Jamaica was responsible for 43 percent of its own financing – and an inequity in Jamaica’s proportional representation in the federation’s House of Assembly. Manley’s PNP favoured staying in the federation, but he agreed to hold a referendum in September 1961 to decide on the issue. When 54 percent of the electorate voted to withdraw, Jamaica left the federation, which dissolved in 1962 after Trinidad and Tobago also pulled out. Manley believed that the rejection of his pro-federation policy in the 1961 referendum called for a renewed mandate from the electorate, but the JLP won the election of early 1962 by a fraction. Bustamante assumed the premiership that April, and Manley spent his remaining few years in politics as leader of the opposition.
Jamaica received its independence on 6 August 1962. The new nation retained, however, its membership in the Commonwealth of Nations and adopted a Westminster-style parliamentary system. Bustamante, at the age of 78, became the new nation’s first prime minister.
